Solved Examples: Applied Problems on Derivatives
(1.) WASSCE-FM A boy runs in a line and his displacement at time t seconds
after leaving the start point O is X metres, where $20X = 4t^2 + t^3$.
Find the:
(i.) velocity of the boy when t = 15 seconds;
(ii.) value of t for which the acceleration of the boy is 8 times his initial acceleration.
$ 20X = 4t^2 + t^3 \\[3ex] X = \dfrac{4t^2 + t^3}{20} \\[5ex] X = \dfrac{4t^2}{20} + \dfrac{t^3}{20} \\[5ex] X = \dfrac{1}{5}t^2 + \dfrac{1}{20}t^3 \\[5ex] velocity = v \\[3ex] v = \dfrac{dX}{dt} = 2\left(\dfrac{1}{5}\right) * t + 3\left(\dfrac{1}{20}\right) * t^2 \\[5ex] v = \dfrac{dX}{dt} = \dfrac{2t}{5} + \dfrac{3t^2}{20} \\[5ex] (i.) \\[3ex] v|_{t = 15} = \dfrac{2(15)}{5} + \dfrac{3(15)^2}{20} \\[5ex] v|_{t = 15} = 6 + 33.75 \\[4ex] v|_{t = 15} = 39.75\;m/s \\[5ex] acceleration = a \\[3ex] a = \dfrac{dv}{dt} \\[5ex] a = \dfrac{2}{5} + 2\left(\dfrac{3}{20}\right)^t \\[5ex] a = \dfrac{2}{5} + \dfrac{6t}{20} \\[5ex] \underline{\text{Initial Acceleration}}, a_0 \\[3ex] t = 0 \\[3ex] a_0 = a|_{t = 0} = \dfrac{2}{5} + \dfrac{6(0)}{20} \\[5ex] a_0 = a|_{t = 0} = \dfrac{2}{5} \\[5ex] \text{8 times initial acceleration} = 8\left(\dfrac{2}{5}\right) = \dfrac{16}{5} \\[5ex] (ii.) \\[3ex] a = 8 * a_0 \\[3ex] \dfrac{2}{5} + \dfrac{6t}{20} = \dfrac{16}{5} \\[5ex] \dfrac{6t}{20} = \dfrac{16}{5} - \dfrac{2}{5} \\[5ex] \dfrac{6t}{20} = \dfrac{14}{5} \\[5ex] t = \dfrac{14}{5} * \dfrac{20}{6} \\[5ex] t = 9\dfrac{1}{3}\;seconds $
Find the:
(i.) velocity of the boy when t = 15 seconds;
(ii.) value of t for which the acceleration of the boy is 8 times his initial acceleration.
$ 20X = 4t^2 + t^3 \\[3ex] X = \dfrac{4t^2 + t^3}{20} \\[5ex] X = \dfrac{4t^2}{20} + \dfrac{t^3}{20} \\[5ex] X = \dfrac{1}{5}t^2 + \dfrac{1}{20}t^3 \\[5ex] velocity = v \\[3ex] v = \dfrac{dX}{dt} = 2\left(\dfrac{1}{5}\right) * t + 3\left(\dfrac{1}{20}\right) * t^2 \\[5ex] v = \dfrac{dX}{dt} = \dfrac{2t}{5} + \dfrac{3t^2}{20} \\[5ex] (i.) \\[3ex] v|_{t = 15} = \dfrac{2(15)}{5} + \dfrac{3(15)^2}{20} \\[5ex] v|_{t = 15} = 6 + 33.75 \\[4ex] v|_{t = 15} = 39.75\;m/s \\[5ex] acceleration = a \\[3ex] a = \dfrac{dv}{dt} \\[5ex] a = \dfrac{2}{5} + 2\left(\dfrac{3}{20}\right)^t \\[5ex] a = \dfrac{2}{5} + \dfrac{6t}{20} \\[5ex] \underline{\text{Initial Acceleration}}, a_0 \\[3ex] t = 0 \\[3ex] a_0 = a|_{t = 0} = \dfrac{2}{5} + \dfrac{6(0)}{20} \\[5ex] a_0 = a|_{t = 0} = \dfrac{2}{5} \\[5ex] \text{8 times initial acceleration} = 8\left(\dfrac{2}{5}\right) = \dfrac{16}{5} \\[5ex] (ii.) \\[3ex] a = 8 * a_0 \\[3ex] \dfrac{2}{5} + \dfrac{6t}{20} = \dfrac{16}{5} \\[5ex] \dfrac{6t}{20} = \dfrac{16}{5} - \dfrac{2}{5} \\[5ex] \dfrac{6t}{20} = \dfrac{14}{5} \\[5ex] t = \dfrac{14}{5} * \dfrac{20}{6} \\[5ex] t = 9\dfrac{1}{3}\;seconds $
(2.) USSCE: Advance Mathematics Paper 1 The motion of a particle is described by the law
$s(t) = t^3 - 2t^2 + t + 1$ where t is in seconds and s is in metres.
Its velocity after two (2) seconds is:
$ A.\;\; 5\;m/s \\[3ex] B.\;\; 3\;m/s \\[3ex] C.\;\; 1\;m/s \\[3ex] D.\;\; \text{None of the above} \\[3ex] $
$ Let\;\; velocity = v \\[3ex] s(t) = t^3 - 2t^2 + t + 1 \\[3ex] v = \dfrac{ds}{dt} = 3t^2 - 4t + 1 \\[3ex] After\;\;2\;\;seconds \implies t = 2 \\[3ex] v = 3(2)^2 - 4(2) + 1 \\[3ex] v = 12 - 8 + 1 \\[3ex] v = 5\;m/s $
Its velocity after two (2) seconds is:
$ A.\;\; 5\;m/s \\[3ex] B.\;\; 3\;m/s \\[3ex] C.\;\; 1\;m/s \\[3ex] D.\;\; \text{None of the above} \\[3ex] $
$ Let\;\; velocity = v \\[3ex] s(t) = t^3 - 2t^2 + t + 1 \\[3ex] v = \dfrac{ds}{dt} = 3t^2 - 4t + 1 \\[3ex] After\;\;2\;\;seconds \implies t = 2 \\[3ex] v = 3(2)^2 - 4(2) + 1 \\[3ex] v = 12 - 8 + 1 \\[3ex] v = 5\;m/s $
(3.) MEHA A women's club makes mats and sells them for $73 each.
The cost, in dollars, of making x mats is given by $C(x) = 3.6x^2 + x$
(a) What is the cost of making 15 mats?
(b) Find the formula for the profit made by selling x mats.
(c) Determine the number of mats the club should produce and sell to maximise its profit.
$ C(x) = \text{cost function} \\[3ex] R(x) = \text{revenue function} \\[3ex] P(x) = \text{profit function} \\[3ex] (a) \\[3ex] C(x) = 3.6x^2 + x \\[3ex] C(15) = 3.6(15)^2 + 15 \\[3ex] C(15) = 3.6(225) + 15 \\[3ex] C(15) = \$825.00 \\[3ex] (b) \\[3ex] R(x) = 73 * x = 73x \\[3ex] P(x) = R(x) - C(x) \\[3ex] P(x) = 73x - (3.6x^2 + x) \\[3ex] P(x) = 73x - 3.6x^2 - x \\[3ex] P(x) = -3.6x^2 + 72x \\[3ex] (c) \\[3ex] $ We can solve this question part using at least two approaches.
Vertex Method: the x-coordinate of the vertex gives the number of mats that should be sold to maximise the profit.
The y-coordinate of the vertex gives the maximum profit.
$ \underline\text{{Vertex Method}} \\[3ex] P(x) = -3.6x^2 + 72x \\[3ex] a = -3.6,\;\; b = 72,\;\; c = 0 \\[3ex] x-coordinate \text{ of Vertex} \\[3ex] = -\dfrac{b}{2a} \\[5ex] = -\dfrac{72}{2(-3.6)} \\[5ex] = -\dfrac{72}{-7.2} \\[5ex] = 10 \\[3ex] $ 10 mats should be produced and sold to maximise profit.
$ \underline\text{{Differential Calculus Approach}} \\[3ex] P(x) = -3.6x^2 + 72x \\[3ex] P'(x) = -7.2x + 72 \\[3ex] \text{Set } P'(x) = 0 \text{ and solve for } x \\[3ex] -7.2x + 72 = 0 \\[3ex] -7.2x = -72 \\[3ex] x = \dfrac{-72}{-7.2} \\[5ex] x = 10 \\[3ex] $ 10 mats should be produced and sold to maximise profit.
The cost, in dollars, of making x mats is given by $C(x) = 3.6x^2 + x$
(a) What is the cost of making 15 mats?
(b) Find the formula for the profit made by selling x mats.
(c) Determine the number of mats the club should produce and sell to maximise its profit.
$ C(x) = \text{cost function} \\[3ex] R(x) = \text{revenue function} \\[3ex] P(x) = \text{profit function} \\[3ex] (a) \\[3ex] C(x) = 3.6x^2 + x \\[3ex] C(15) = 3.6(15)^2 + 15 \\[3ex] C(15) = 3.6(225) + 15 \\[3ex] C(15) = \$825.00 \\[3ex] (b) \\[3ex] R(x) = 73 * x = 73x \\[3ex] P(x) = R(x) - C(x) \\[3ex] P(x) = 73x - (3.6x^2 + x) \\[3ex] P(x) = 73x - 3.6x^2 - x \\[3ex] P(x) = -3.6x^2 + 72x \\[3ex] (c) \\[3ex] $ We can solve this question part using at least two approaches.
Vertex Method: the x-coordinate of the vertex gives the number of mats that should be sold to maximise the profit.
The y-coordinate of the vertex gives the maximum profit.
$ \underline\text{{Vertex Method}} \\[3ex] P(x) = -3.6x^2 + 72x \\[3ex] a = -3.6,\;\; b = 72,\;\; c = 0 \\[3ex] x-coordinate \text{ of Vertex} \\[3ex] = -\dfrac{b}{2a} \\[5ex] = -\dfrac{72}{2(-3.6)} \\[5ex] = -\dfrac{72}{-7.2} \\[5ex] = 10 \\[3ex] $ 10 mats should be produced and sold to maximise profit.
$ \underline\text{{Differential Calculus Approach}} \\[3ex] P(x) = -3.6x^2 + 72x \\[3ex] P'(x) = -7.2x + 72 \\[3ex] \text{Set } P'(x) = 0 \text{ and solve for } x \\[3ex] -7.2x + 72 = 0 \\[3ex] -7.2x = -72 \\[3ex] x = \dfrac{-72}{-7.2} \\[5ex] x = 10 \\[3ex] $ 10 mats should be produced and sold to maximise profit.
(4.) JAMB A trader realizes $10x - x^2$ naira profit from the sale of x bags of corn.
How many bags will give him the maximum profit?
$ A.\;\; 4 \\[3ex] B.\;\; 5 \\[3ex] C.\;\; 6 \\[3ex] D.\;\; 7 \\[3ex] $
We can solve this question part using at least two approaches.
Vertex Method: the x-coordinate of the vertex is the number of bags that will give the maximum profit.
The y-coordinate of the vertex is the maximum profit.
$ \underline\text{{Vertex Method}} \\[3ex] y = 10x - x^2 \\[3ex] y = -x^2 + 10x \\[3ex] y = ax^2 + bx + c \\[3ex] a = -1, b = 10 \\[3ex] x-coordinate \text{ of Vertex} \\[3ex] = -\dfrac{b}{2a} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{-10}{2(-1)} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{-10}{-2} \\[5ex] = 5 \\[3ex] $ The sale of 5 bags will give the maximum profit.
$ \underline\text{{Differential Calculus Approach}} \\[3ex] y = 10x - x^2 \\[3ex] \dfrac{dy}{dx} = 10 - 2x \\[3ex] 10 - 2x = 0 \\[3ex] 10 = 2x \\[3ex] 2x = 10 \\[3ex] x = \dfrac{10}{2} \\[3ex] x = 5 \\[3ex] $ The sale of 5 bags will give the maximum profit.
How many bags will give him the maximum profit?
$ A.\;\; 4 \\[3ex] B.\;\; 5 \\[3ex] C.\;\; 6 \\[3ex] D.\;\; 7 \\[3ex] $
We can solve this question part using at least two approaches.
Vertex Method: the x-coordinate of the vertex is the number of bags that will give the maximum profit.
The y-coordinate of the vertex is the maximum profit.
$ \underline\text{{Vertex Method}} \\[3ex] y = 10x - x^2 \\[3ex] y = -x^2 + 10x \\[3ex] y = ax^2 + bx + c \\[3ex] a = -1, b = 10 \\[3ex] x-coordinate \text{ of Vertex} \\[3ex] = -\dfrac{b}{2a} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{-10}{2(-1)} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{-10}{-2} \\[5ex] = 5 \\[3ex] $ The sale of 5 bags will give the maximum profit.
$ \underline\text{{Differential Calculus Approach}} \\[3ex] y = 10x - x^2 \\[3ex] \dfrac{dy}{dx} = 10 - 2x \\[3ex] 10 - 2x = 0 \\[3ex] 10 = 2x \\[3ex] 2x = 10 \\[3ex] x = \dfrac{10}{2} \\[3ex] x = 5 \\[3ex] $ The sale of 5 bags will give the maximum profit.
(5.) You have a pond with fish.
You feed the fish with f kg fish food monthly.
You have noticed that the number N of fish living in your pond depends on the amount of feed.
You have even worked out a formula: $N = -f^2 + 8f + 5$
(a.) According to this function, if you stop feeding your fish, will they all die?
(b.) What amount of feed will give you the greatest amount of fish?
(c.) What is the greatest amount of fish at any given time?
(d.) Calculate the gradient function $\dfrac{dN}{df}$ for $f = 2$.
Explain what this value tells you about the development of the number of your fish.
$ N(f) = -f^2 + 8f + 5 \\[3ex] (a.) \\[3ex] f = 0 ...\text{no more feed for the fish} \\[3ex] N(0) = -0^2 + 8(0) + 5 \\[3ex] N(0) = 5 \\[3ex] $ According to this function, if you stop feeding the fish, they will not all die.
5 fish will remain.
The function is a quadratic function, so let us find the vertex.
The amount of feed will give you the greatest amount of fish is the x-coordinate of the vertex.
The greatest amount of fish is the y-coordinate of the vertex.
$ N(f) = -f^2 + 8f + 5 \\[3ex] \text{Compare to the standard form: } N(f) = af^2 + bf + c \\[3ex] a = -1 \\[3ex] b = 8 \\[3ex] c = 5 \\[3ex] x-coordinate = -\dfrac{b}{2a} \\[5ex] = -\dfrac{8}{2(-1)} \\[5ex] = 4\;kg \\[5ex] y-coordinate = N(4) \\[3ex] = -4^2 + 8(4) + 5 \\[3ex] = 21\;fish \\[3ex] $ (b.) The amount of feed that gives the greatest amount of fish is 4kg per month.
(c.) The greatest amount of fish at any given time is 21 fish.
$ (d.) \\[3ex] N(f) = -f^2 + 8f + 5 \\[3ex] \dfrac{dN}{df} = -2f + 8 \\[5ex] \left.\dfrac{dN}{df}\right|_{f = 2} \\[5ex] = -2(2) + 8 \\[3ex] = 4 \\[3ex] $ The instantaneous rate of change in the number of fish when the amount of feed is 2 kg, is 4 fish per kilogram of feed.
This implies that at the feeding level of 2 kg per feed monthly, each additional kilogram of feed would increase the fish population at a rate of about 4 fish.
You feed the fish with f kg fish food monthly.
You have noticed that the number N of fish living in your pond depends on the amount of feed.
You have even worked out a formula: $N = -f^2 + 8f + 5$
(a.) According to this function, if you stop feeding your fish, will they all die?
(b.) What amount of feed will give you the greatest amount of fish?
(c.) What is the greatest amount of fish at any given time?
(d.) Calculate the gradient function $\dfrac{dN}{df}$ for $f = 2$.
Explain what this value tells you about the development of the number of your fish.
$ N(f) = -f^2 + 8f + 5 \\[3ex] (a.) \\[3ex] f = 0 ...\text{no more feed for the fish} \\[3ex] N(0) = -0^2 + 8(0) + 5 \\[3ex] N(0) = 5 \\[3ex] $ According to this function, if you stop feeding the fish, they will not all die.
5 fish will remain.
The function is a quadratic function, so let us find the vertex.
The amount of feed will give you the greatest amount of fish is the x-coordinate of the vertex.
The greatest amount of fish is the y-coordinate of the vertex.
$ N(f) = -f^2 + 8f + 5 \\[3ex] \text{Compare to the standard form: } N(f) = af^2 + bf + c \\[3ex] a = -1 \\[3ex] b = 8 \\[3ex] c = 5 \\[3ex] x-coordinate = -\dfrac{b}{2a} \\[5ex] = -\dfrac{8}{2(-1)} \\[5ex] = 4\;kg \\[5ex] y-coordinate = N(4) \\[3ex] = -4^2 + 8(4) + 5 \\[3ex] = 21\;fish \\[3ex] $ (b.) The amount of feed that gives the greatest amount of fish is 4kg per month.
(c.) The greatest amount of fish at any given time is 21 fish.
$ (d.) \\[3ex] N(f) = -f^2 + 8f + 5 \\[3ex] \dfrac{dN}{df} = -2f + 8 \\[5ex] \left.\dfrac{dN}{df}\right|_{f = 2} \\[5ex] = -2(2) + 8 \\[3ex] = 4 \\[3ex] $ The instantaneous rate of change in the number of fish when the amount of feed is 2 kg, is 4 fish per kilogram of feed.
This implies that at the feeding level of 2 kg per feed monthly, each additional kilogram of feed would increase the fish population at a rate of about 4 fish.
(6.)
(7.)
(8.)
(9.)
(10.)
(11.)
(12.)
(13.)
(14.)
(15.)
(16.)
(17.)
(18.)
(19.)
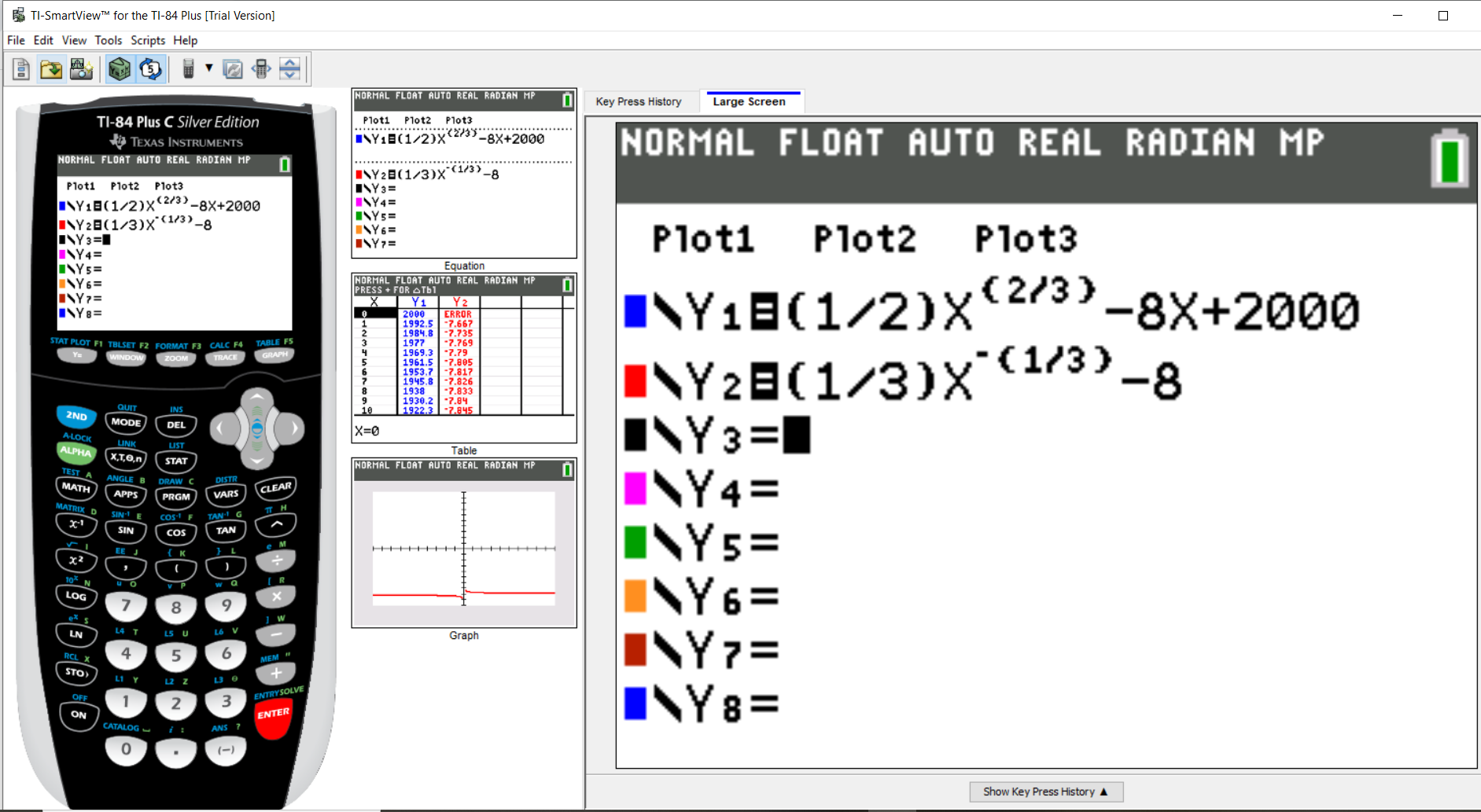
(20.) Assume the cost for publishing a book is modelled by the function:
$C(x) = 2000 + 14x + \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}}$
Use Newton's method to determine the break-even point if the selling price of the book is $22.00
Take the initial guess as 125
Round your answer to the nearest integer.
$ \underline{\text{Break-even Point}} \\[3ex] cost = revenue \\[3ex] cost = C(x) = 2000 + 14x + \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} \\[7ex] revenue = R(x) = 22 * x = 22x \\[3ex] \implies \\[3ex] 2000 + 14x + \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} = 22x \\[7ex] 2000 + 14x - 22x + \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} = 0 \\[7ex] 2000 - 8x + \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} = 0 \\[7ex] \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8x + 2000 = 0 \\[7ex] \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8x + 2000 = f(x) \\[7ex] f(x) = \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8x + 2000 \\[7ex] f'(x) = \dfrac{2}{3}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\left(x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 1\right) - 8 \\[7ex] f'(x) = \dfrac{1}{3}x^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8 \\[7ex] x_{n + 1} = x_n - \dfrac{f(x)}{f'(x)} \\[5ex] \implies \\[3ex] x_{n + 1} = x_n - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}x_n^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8x_n + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3}x_n^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8} \\[9ex] x_1 = 125 \\[3ex] x_2 = x_1 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* x_1^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8 * x_1 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * x_1^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8} \\[9ex] x_2 = 125 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* 125^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8 * 125 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * 125^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8} \\[9ex] x_2 = 125 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* (\sqrt[3]{125})^2 - 8 * 125 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * (\sqrt[3]{125})^{-1} - 8} \\[7ex] x_2 = 125 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* 5^2 - 8 * 125 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * 5^{-1} - 8} \\[7ex] x_2 = 125 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* 25 - 8 * 125 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * \dfrac{1}{5} - 8} \\[7ex] x_2 = 125 - \dfrac{12.5 - 1000 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{15} - 8} \\[7ex] x_2 = 125 - \left(1012.5 \div -\dfrac{119}{15}\right) \\[5ex] x_2 = 125 - \left(1012.5 * -\dfrac{15}{119}\right) \\[5ex] x_2 = 125 - -\dfrac{15187.5}{119} \\[5ex] x_2 = 125 + 127.6260504 \\[3ex] x_2 = 252.6260504 \\[5ex] x_3 = x_2 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* x_2^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8 * x_2 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * x_2^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8} \\[9ex] x_3 = 252.6260504 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* 252.6260504^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8 * 252.6260504 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * 252.6260504^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8} \\[5ex] $
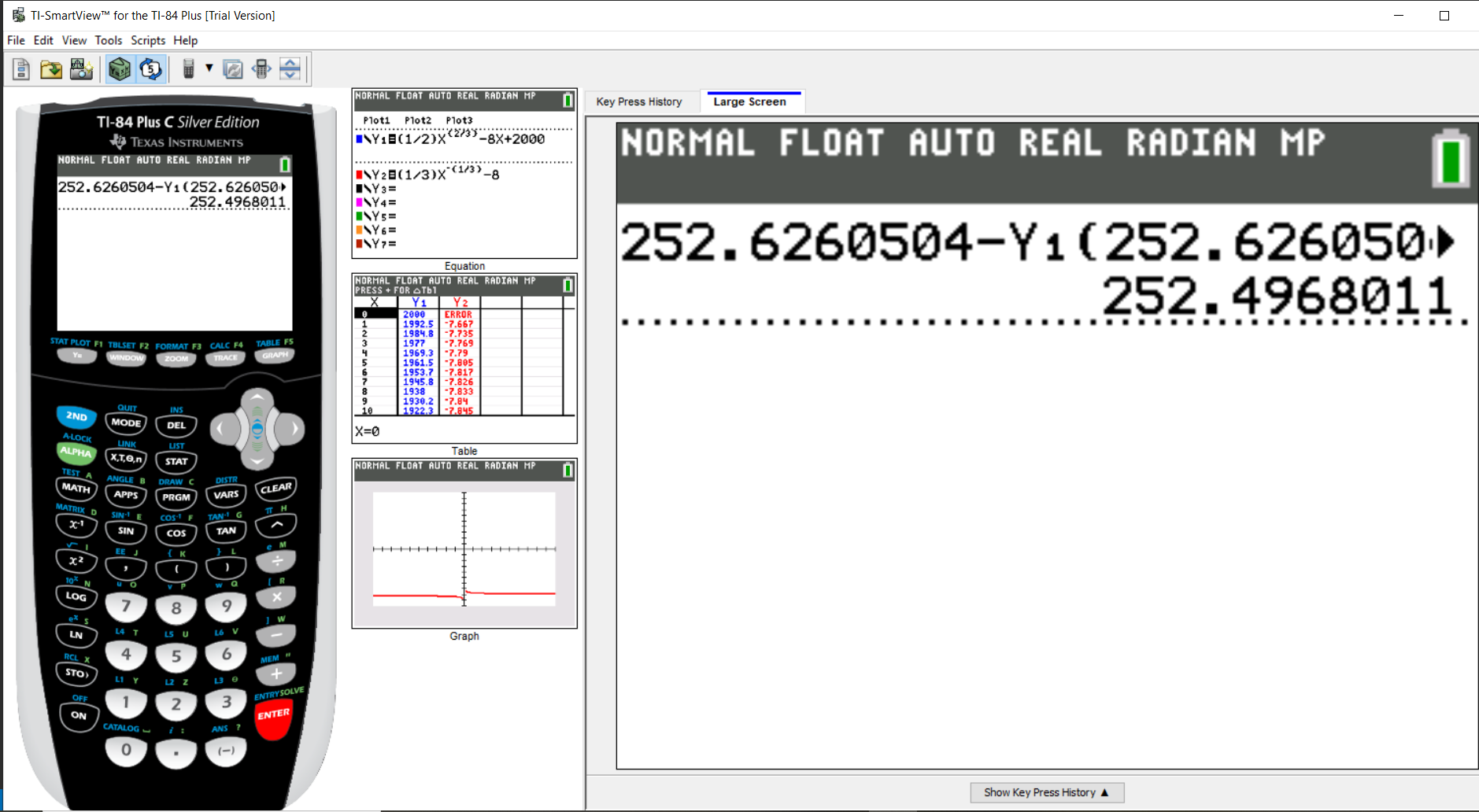
$ x_3 = 252.4968011 \\[3ex] $
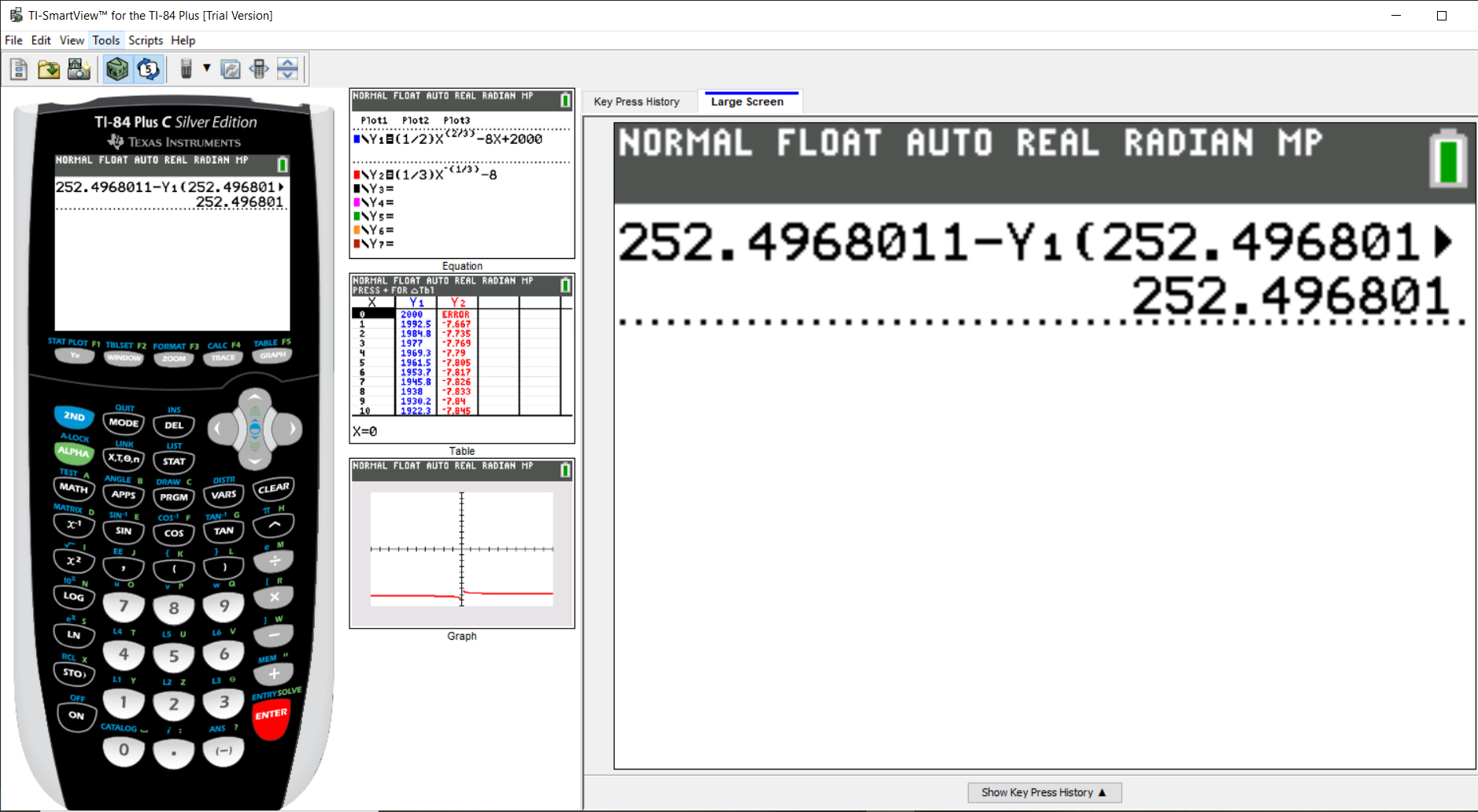
$ x_4 = 252.496801 \\[3ex] x_4 \approx x_3...STOP \\[3ex] \implies \\[3ex] x \approx 252 \\[3ex] $ The break-even point is approximately 252 books.
Use Newton's method to determine the break-even point if the selling price of the book is $22.00
Take the initial guess as 125
Round your answer to the nearest integer.
$ \underline{\text{Break-even Point}} \\[3ex] cost = revenue \\[3ex] cost = C(x) = 2000 + 14x + \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} \\[7ex] revenue = R(x) = 22 * x = 22x \\[3ex] \implies \\[3ex] 2000 + 14x + \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} = 22x \\[7ex] 2000 + 14x - 22x + \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} = 0 \\[7ex] 2000 - 8x + \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} = 0 \\[7ex] \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8x + 2000 = 0 \\[7ex] \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8x + 2000 = f(x) \\[7ex] f(x) = \dfrac{1}{2}x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8x + 2000 \\[7ex] f'(x) = \dfrac{2}{3}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\left(x^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 1\right) - 8 \\[7ex] f'(x) = \dfrac{1}{3}x^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8 \\[7ex] x_{n + 1} = x_n - \dfrac{f(x)}{f'(x)} \\[5ex] \implies \\[3ex] x_{n + 1} = x_n - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}x_n^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8x_n + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3}x_n^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8} \\[9ex] x_1 = 125 \\[3ex] x_2 = x_1 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* x_1^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8 * x_1 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * x_1^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8} \\[9ex] x_2 = 125 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* 125^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8 * 125 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * 125^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8} \\[9ex] x_2 = 125 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* (\sqrt[3]{125})^2 - 8 * 125 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * (\sqrt[3]{125})^{-1} - 8} \\[7ex] x_2 = 125 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* 5^2 - 8 * 125 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * 5^{-1} - 8} \\[7ex] x_2 = 125 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* 25 - 8 * 125 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * \dfrac{1}{5} - 8} \\[7ex] x_2 = 125 - \dfrac{12.5 - 1000 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{15} - 8} \\[7ex] x_2 = 125 - \left(1012.5 \div -\dfrac{119}{15}\right) \\[5ex] x_2 = 125 - \left(1012.5 * -\dfrac{15}{119}\right) \\[5ex] x_2 = 125 - -\dfrac{15187.5}{119} \\[5ex] x_2 = 125 + 127.6260504 \\[3ex] x_2 = 252.6260504 \\[5ex] x_3 = x_2 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* x_2^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8 * x_2 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * x_2^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8} \\[9ex] x_3 = 252.6260504 - \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}* 252.6260504^{\dfrac{2}{3}} - 8 * 252.6260504 + 2000}{\dfrac{1}{3} * 252.6260504^{-\dfrac{1}{3}} - 8} \\[5ex] $


$ x_3 = 252.4968011 \\[3ex] $

$ x_4 = 252.496801 \\[3ex] x_4 \approx x_3...STOP \\[3ex] \implies \\[3ex] x \approx 252 \\[3ex] $ The break-even point is approximately 252 books.
(21.)